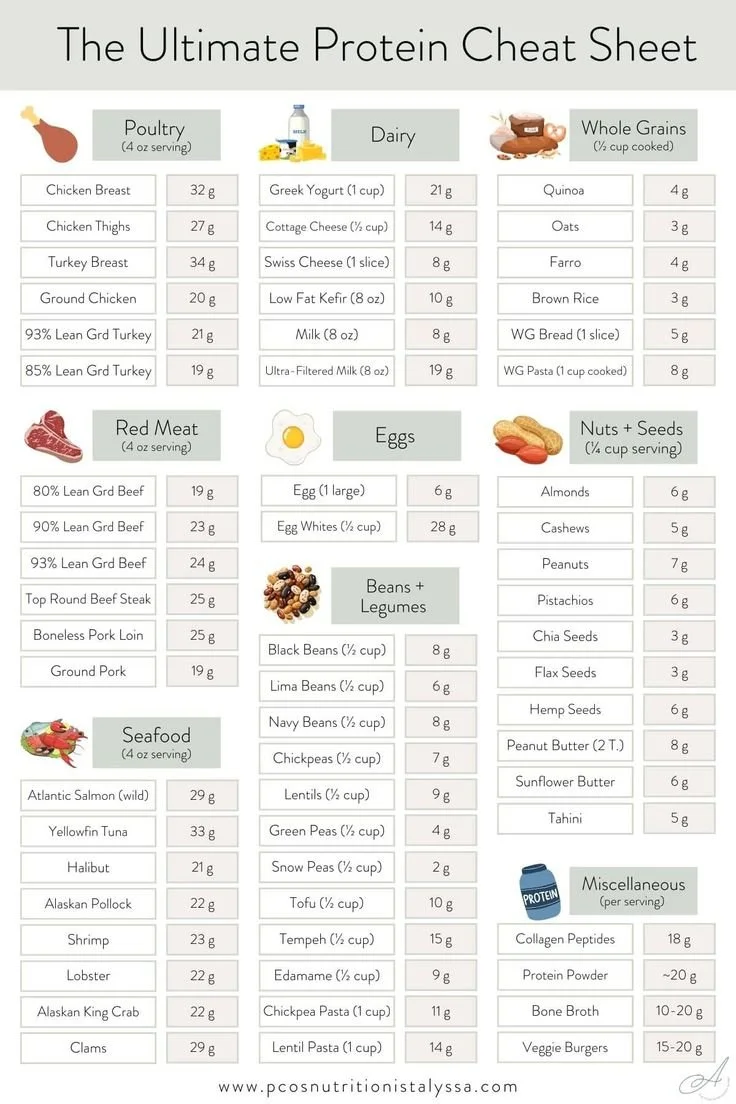
Nutrition
Focuses on the consumption of food and its impact on health. It covers healthy eating habits, balanced diets, meal plans, specific diet types (like keto or vegan), superfoods, weight management, and nutritional advice.
More stories
Load More
Congratulations. You've reached the end of the internet.